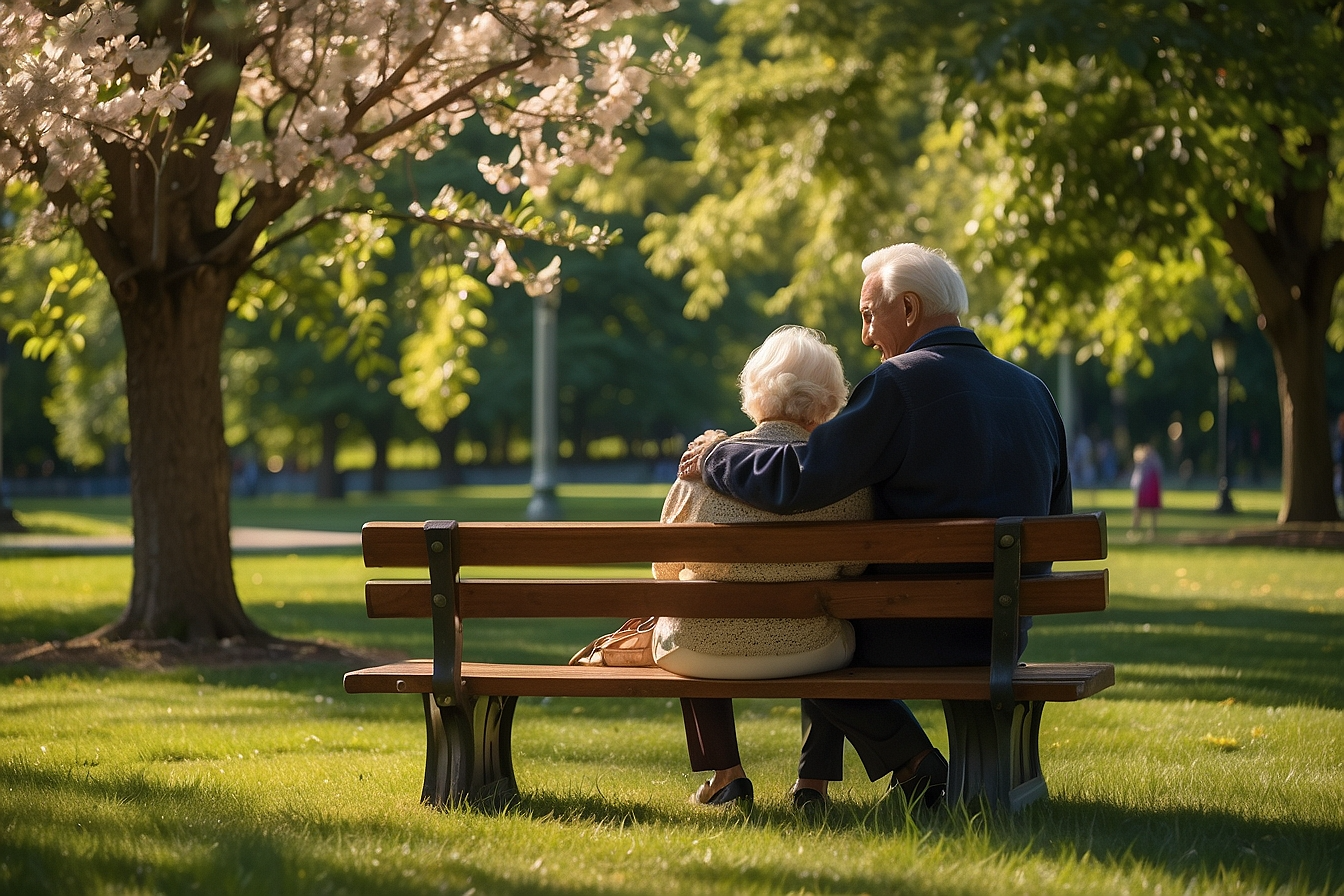
Imagine a warm, sunny afternoon where you sit on a park bench, chatting with Margaret, an energetic and wise 82-year-old with sparkling eyes and a lifetime of stories. As she shares tales of her youth, challenges, and triumphs, you’re struck by the depth of her wisdom and the journey she’s embarked on to reach this stage of her life. This moment of connection highlights a profound truth: the journey through life doesn’t taper off as we age; it simply evolves, bringing new needs and aspirations to the forefront.
Margaret’s story vividly shows how humanistic psychology illustrates a universal journey, underscoring the significance of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in understanding the shifting priorities and challenges the elderly face. As we delve into the complexities of aging, we find that the essence of human motivation and fulfillment transcends age. This anecdote sets the stage for our exploration of how we can support the well-being of the elderly by applying the timeless principles of Maslow’s theory, ensuring that every Margaret out there has the opportunity to thrive in her golden years.
Understanding Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
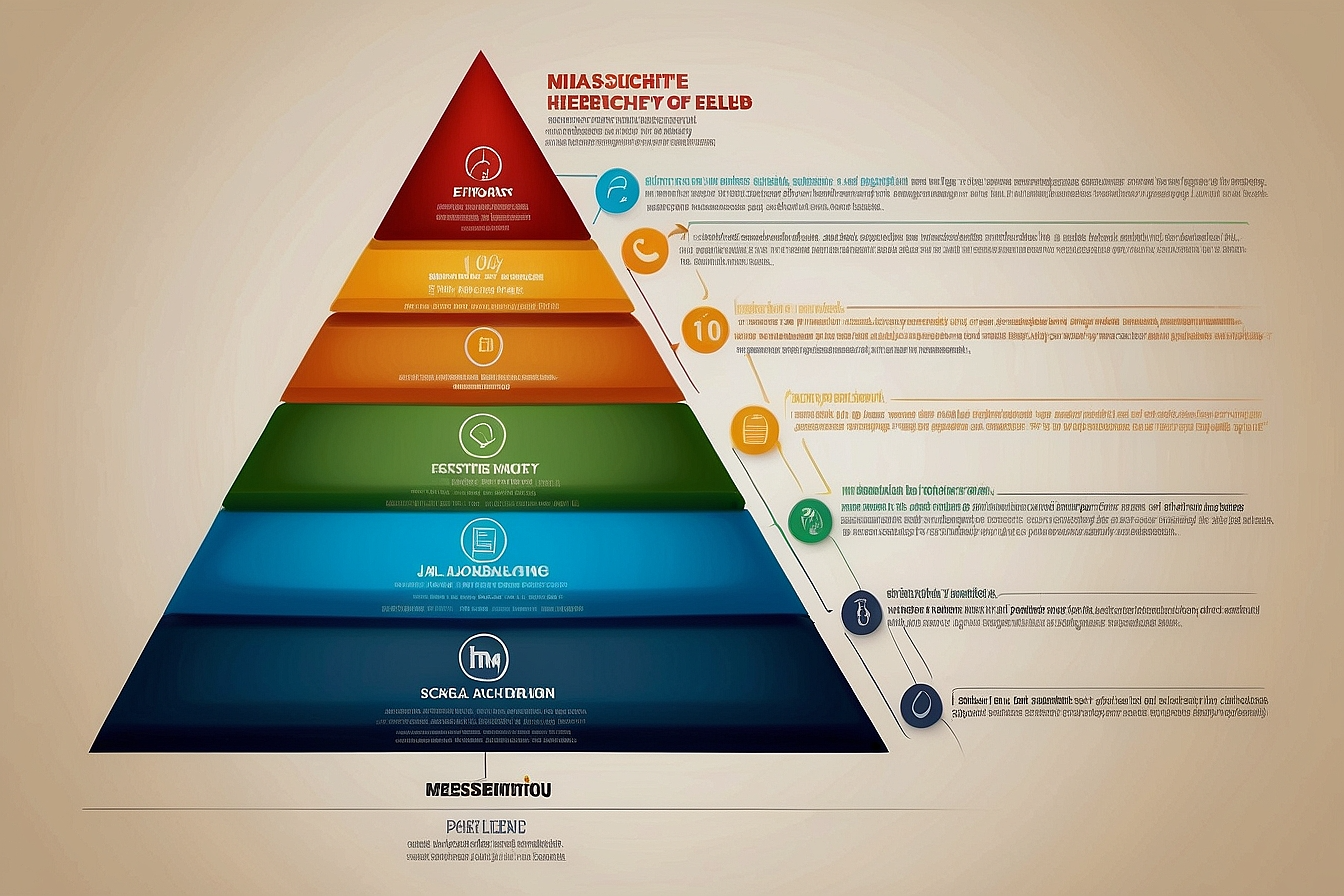
At the heart of the psychological science of human motivation lies a simple yet profound framework: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Psychologist Abraham Maslow developed this theory in the middle of the 20th century and contends that an innate desire to satisfy several needs, from the most fundamental to the most complex, drives our actions. Let’s break down the five levels of this hierarchy and explore the pinnacle of human development: self-actualization.
The 5 Levels of Needs
- Physiological Needs: These are the pyramid’s foundation and include necessities for human survival, such as air, water, food, shelter, and sleep. Without these, the human body cannot function properly.
- Safety Needs: Once physiological needs are met, the focus shifts to safety and security. This level encompasses personal safety, employment, health, and property security.
- Social Needs: Humans are inherently social beings. This layer involves the need for belongingness, love, and interpersonal relationships. Friends, family, and intimacy play crucial roles here.
- Esteem Needs: Esteem needs are about achieving and gaining respect and self-esteem. This tier is divided into respect for others (status, recognition) and self-respect (self-esteem, confidence).
- Self-Actualization: At the peak of Maslow’s pyramid lies self-actualization, realizing one’s potential, self-fulfillment, seeking personal growth, and peak experiences. It represents becoming everything one is capable of becoming.
Importance of Self-Actualization
Self-actualization is not just a destination but a journey of continuous growth and exploration of individual differences. It is where individuals strive to achieve their full potential and engage in activities that enrich their sense of self and overall life satisfaction. This stage is particularly poignant when considering the elderly, as it emphasizes the ongoing capacity for personal development, creativity, and meaningful engagement with the world, regardless of age.
Maslow’s theory highlights that the journey toward self-actualization is universal, transcending age and time. Understanding these needs is crucial in appreciating the diverse experiences aesthetic needs and aspirations of the elderly, paving the way for a more supportive and enriching environment that honors their journey toward self-actualization.
Meeting Basic Needs for the Elderly

The foundation of well-being for human beings at any age begins with meeting essential physiological needs. For the elderly, ensuring these needs are met with care and dignity is crucial for their overall health and quality of life. Here, we focus on two fundamental aspects: proper nutrition and hydration and a safe and comfortable living environment.
Ensuring Proper Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration are pivotal for maintaining the health of the elderly. As the body ages, nutritional requirements change, and the risk of dehydration increases. To address these challenges:
- Personalized Nutrition Plans: Individual dietary needs, health conditions, and preferences must be considered. Nutrition plans should include nutrient-dense foods, adequate fiber, and hydration strategies to ensure elders receive balanced meals that cater to their specific health requirements.
- Assistance and Monitoring: For those who may struggle with meal preparation or have difficulty consuming food due to health issues, providing assistance and regular monitoring can help prevent malnutrition and dehydration.
Providing a Safe and Comfortable Living Environment
A safe and comfortable living environment is crucial for the elderly, significantly impacting their safety and overall well-being.
- Adaptations and Modifications: Homes and living spaces should be adapted to reduce fall risks and accommodate physical limitations. This includes installing grab bars, ensuring good lighting, and removing tripping hazards.
- Access to Medical Care and Emergency Services: It is vital to ensure that the elderly have easy access to medical care and emergency services. This can be facilitated through in-home care services, emergency alert systems, and regular health check-ups.
- Comfort and Familiarity: Beyond physical safety, the living environment should offer comfort and a sense of belonging. Personal touches, such as family photos and familiar furnishings, can significantly improve a person’s sense of security and well-being.
Addressing these basic needs can help the elderly survive and thrive, providing a solid foundation to continue building a fulfilling life. Ensuring that our elders’ fundamental physiological and safety needs are respected and cared for reflects our society’s values and commitment to every individual’s dignity and well-being.
Fulfilling Social Needs
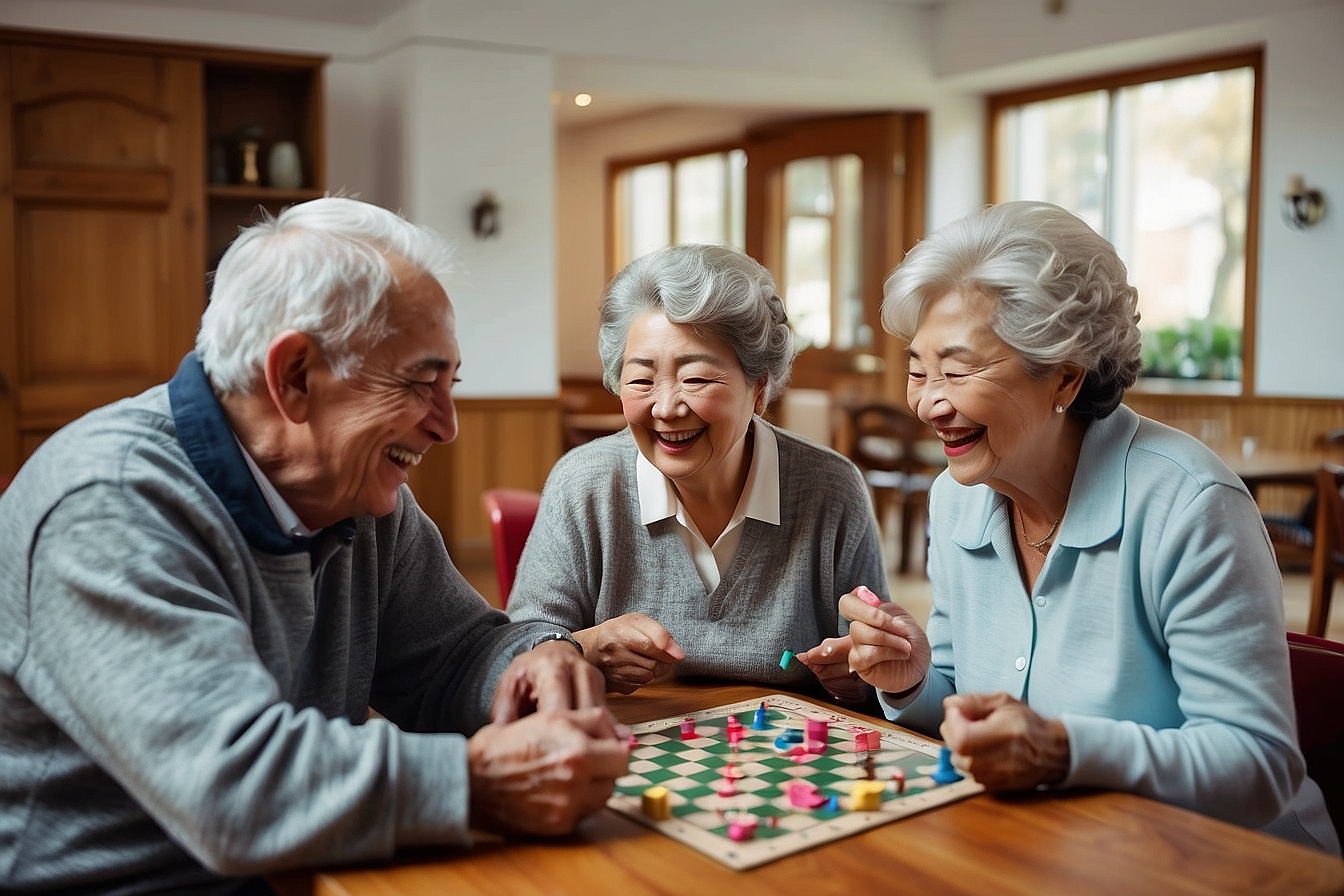

The importance of fulfilling social needs for the elderly cannot be overstated. Social connections and relationships provide emotional support, reduce stress, and improve life quality. However, many older adults face challenges in maintaining these connections, leading to social isolation. Addressing these needs is crucial for their emotional and psychological well-being.
Encouraging Social Connections and Relationships
Creating opportunities for the elderly to engage with others and foster meaningful relationships is essential. Here are some strategies to encourage social connections:
- Community Programs and Activities: Local community centers often offer programs specifically designed for seniors, such as art classes, exercise groups, and social clubs. These activities provide a platform for the elderly to interact and form new friendships.
- Technology as a Bridge: In today’s digital age, technology can significantly keep the elderly connected with their families and friends. Teaching them to use social media, video calls, and other communication tools can help bridge the gap between generations and reduce feelings of loneliness.
- Volunteer Opportunities: Volunteer work allows older adults to feel valued and connected to their community. It provides a sense of purpose and offers the chance to meet people with similar interests.
Addressing Social Isolation
Social isolation can significantly affect the health and happiness of the elderly. It’s essential to recognize the signs of isolation and take steps to mitigate them:
- Regular Check-Ins: Family, friends, and caregivers should ensure regular contact with the elderly, whether through visits, phone calls, or other means of communication. These check-ins can make a big difference in their overall well-being.
- Transportation Solutions: Mobility issues can hinder the elderly from participating in social activities. Providing transportation solutions, such as community shuttle services or assistance with arranging rides, can help them remain active and engaged.
- Encourage Inter-generational Interaction: Programs that promote interaction between the elderly and younger generations can be incredibly beneficial. These interactions can provide fresh perspectives, reduce age-related stereotypes, and foster mutual respect and understanding.
By actively working to fulfill the social needs of the elderly, we contribute to their sense of belonging and emotional well-being. Encouraging social psychology and facilitating social connections and addressing the challenges of social isolation are key to supporting older adults in leading happier, more fulfilling lives.
Promoting Self-Esteem and Personal Growth
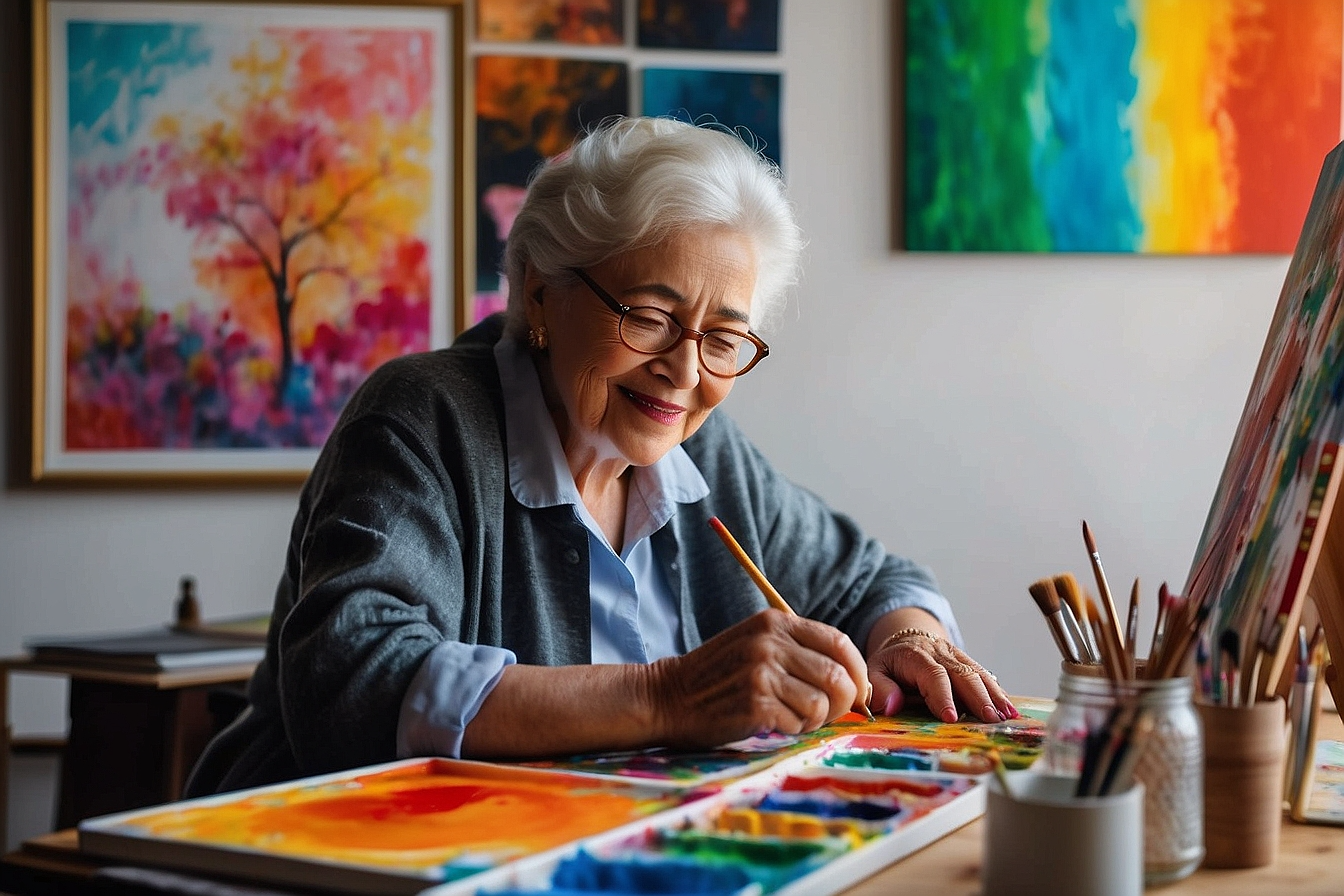

As individuals age, maintaining self-esteem and pursuing personal growth remain integral to their well-being. The elderly, with their wealth of experience and knowledge, have much to offer and achieve. Opportunities that promote self-worth and allow for continued learning, growth needs and development can enrich this stage of life.
Encouraging Activities to Maintain Self-Worth
Activities that promote a sense of accomplishment good self esteem and recognition are vital in supporting the self-esteem of the elderly. Consider the following approaches:
- Skill-Sharing and Mentoring: Many older adults possess specialized skills and life experiences that are invaluable to younger generations. Encouraging them to mentor or teach others allows them to share this wealth of knowledge and reinforces their sense of value and self-worth.
- Creative Expression: Engaging in artistic activities such as painting, writing, music, or craftwork enables the elderly to express themselves and gain a sense of achievement. Exhibitions or performances can further recognize their talents.
- Participation in Decision Making: Involving older adults in decisions that affect their lives, whether in a family setting or a community group, affirms their importance and contribution, bolstering their self-esteem.
Supporting Continued Learning and Development
The pursuit of knowledge and personal interests should not diminish with age. Supporting the elderly in continued learning and development can greatly enhance their quality of life:
- Educational Workshops and Classes: Many community centers, libraries, and educational institutions offer workshops, courses, and lectures suitable for the elderly. These can range from academic subjects to practical life skills, providing mental stimulation and opportunities for personal growth.
- Technology Training: With the rapid advancement of technology, offering training sessions can help older adults stay connected and up to date. Learning to navigate the internet, use social media, or operate new devices can open up new worlds for them.
- Encouraging Physical Activity: Physical activities, tailored to their abilities, benefit their health and promote mental well-being. Yoga, tai chi, walking clubs, and swimming foster physical and mental resilience.
Promoting activities that enhance self-esteem and personal growth contributes significantly to the emotional and psychological health of the elderly. By recognizing their potential for continued development and providing opportunities to engage in fulfilling activities, society can help older adults lead vibrant, meaningful lives. This enriches their experience and strengthens their connection to the community, affirming their valuable role in society.
Challenges in Meeting the Needs of the Elderly

While striving to support the well-being of the elderly is a noble goal, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges that may impede fulfilling their needs. Physical limitations, health issues, emotional and mental well-being, and financial constraints can significantly affect their quality of life. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward addressing them effectively.
Physical Limitations and Health Issues
As individuals age, they may encounter a range of health issues, cognitive needs and physical limitations that can hinder their ability to meet basic needs, engage socially, and pursue personal growth activities:
- Mobility Issues: Problems with mobility can limit an elderly person’s ability to perform daily tasks, access services, and participate in community activities, leading to increased dependence on others.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, heart conditions, and dementia are more prevalent in older age and require ongoing management, which can be both physically and emotionally taxing.
Addressing Emotional and Mental Well-Being
Emotional and mental health is as crucial as physical health, yet it’s often overlooked in the elderly. Several factors contribute to this challenge:
- Isolation and Loneliness: These feelings can lead to significant mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. Losing friends, family, and a sense of purpose can exacerbate these feelings.
- Cognitive Decline: Conditions like Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia affect cognitive function, making it difficult for individuals to engage fully in life and maintain their independence.
Financial Constraints
Financial security is a significant concern for many elderly individuals, affecting their ability to access necessary health care, nutritious food, and safe living conditions:
- Fixed Income: Many older adults live on fixed incomes from pensions or savings, which may not keep pace with the cost of living, healthcare, and inflation.
- Healthcare Costs: Even with insurance, the cost of healthcare, including medications, treatments, and long-term care needs, can be prohibitive.
Overcoming These Challenges
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving individual, community, and governmental efforts:
- Accessible Healthcare and Support Services: It is essential to ensure that older adults have access to affordable healthcare and support services that address both their physical and mental health needs.
- Community and Social Support: Building strong support networks through community programs, volunteer services, and family engagement can help reduce isolation and improve emotional well-being.
- Financial Assistance Programs: Governments and organizations can offer financial assistance and subsidies for healthcare, housing, and essential services to alleviate the burden on the elderly.
Understanding and actively addressing the challenges faced by the elderly is crucial in ensuring they receive the support and care needed to live fulfilling lives. By recognizing the barriers to meeting their needs, society can work towards more inclusive and supportive strategies that honor and respect the dignity of every older individual.
Conclusion

According to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, the journey through the golden years is characterized by a distinct set of needs and difficulties. Understanding these layers—from basic physiological necessities to the pinnacle of self-actualization—sheds light on the holistic approach required to support the well-being of the elderly. As we’ve explored, meeting these needs involves more than just addressing physical health; it encompasses fostering social connections, encouraging personal growth, and overcoming significant barriers such as physical limitations, emotional struggles, and financial constraints.
The stories and experiences of our elders, like Margaret sitting on a park bench sharing her wisdom, remind us of the rich tapestry of life they represent. They highlight the importance of nurturing their dignity, independence, and joy during their later years. Society, communities, families, and individuals all have roles to play in our human needs and in creating an environment that supports the elderly in achieving a sense of fulfillment and well-being.
By promoting activities that enhance self-esteem, facilitating continued learning and development, and addressing the multifaceted challenges the elderly face, we can contribute to a world where aging is not just about growing old but about embracing the opportunities for growth, connection, and self-discovery that the later years can bring.
The elderly have given much to society, shaping the world with their knowledge, skills, and experiences. It’s our shared responsibility to ensure that their needs are met with compassion, respect, and action. By doing so, we enrich their lives and deepen our understanding of human behavior and appreciation of life’s journey, reinforcing the bond of humanity that connects us all.

